
Home >> Fibre Optic Cables
Fibre Optic Cables Suppliers
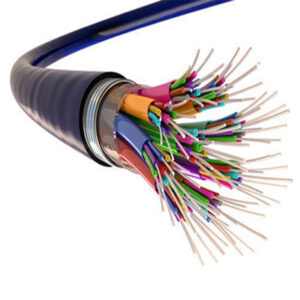

A Fiber-Optic Cable, also known as an Fiber-Optic Cable, is an assembly similar to an electrical cable, but containing one or more optical fibers that are used to carry light. The optical fiber elements are typically individually coated with plastic layers and contained in a protective tube suitable for the environment where the cable is used. Different types of cable are used for different applications, for example, long distance telecommunication, or providing a high-speed data connection between different parts of a building.
The need to stay always connected, for individuals as well as for enterprises, has set the demand rolling for high internet speeds with high quality and consistency. Further, innovations in the telecom sector have increased the deployment of broadband-based network architectures. This all has given a huge growth opportunity for the Fiber Optic Cable (OFC) industry.
The Science behind Fibre Optic Cables
Optical Fibre is hair-thin material made of glass. Generally, optical fiber has a diameter of 125 micrometers (μm), which is actually the diameter of the cladding, or outer reflecting layer. The core, or inner transmitting cylinder, may have a much smaller diameter (sometimes 10 μm). Through the process of total internal reflection, light rays are reflected into the fibers within the core. This can happen for great distances with little attenuation or reduction in density. The degree of attenuation varies according to the wavelength, with little attenuation in intensity.
What is optical fiber optic cable?
A fiber-optic cable is composed of very thin strands of glass or plastic known as Optical Fibers; one cable can have as few as two strands or as many as several hundreds of them. These Fiber-Optic Cable cables carry information in the form of data between two places using optical or light-based technology. Once the light beams travel down the optical Fiber-Optic Cable (OFC), they would emerge at the other end. A photoelectric cell will be required to turn the pulses of light back into electrical information the computer can understand.
While traveling down fiber optic cable, light bounces repeatedly off the walls. The beam of light does not leak out of the edges because it hits the glass at really shallow angles. And then it reflects back again as if the glass were really a mirror. This is called total internal reflection. The other factor that keeps it in the pipe is the cable structure.
Fiber-optic cable offers many advantages, the prime ones being higher bandwidth and reach. Optical fibre cables (OFC) are now preferred over old copper telecom cables as they provide high-speed broadband services. Fiber-optic cable loses 3% of the signal over 100 meters of distance, while copper wires lose 94%. Additionally, optical fibres are more long-lasting as compared to copper wires, which are much more fragile. Copper wire can be tapped very easily, while optical fibres do not radiate signals that can be tapped. Fiber-optic cable offers much lower latency (the amount of time required to perform data transmission) compared to copper wires.
What is optical fiber cable used for?
The Indian optical fiber cable market is gaining traction. The growth is driven by continued investments being made by the Indian government in developing OFC network infrastructure, in various projects. The Indian market for optical fibre cable (OFC) is projected to grow at a CAGR of 17% through 2023. There has been increased adoption of Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) connectivity owing to government initiatives such as Digital India, Smart Cities, or Bharatnet. Moreover, the growing number of data centers in India will fuel this growth further.
We are wild range of Fibre Optic Cables Suppliers in Kolkata Market.

